If you create and administer backups, you will have heard the terms application-consistent backup and Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS). You may even know that VSS runs in the background while a backup takes place. Knowing that is usually enough but if you’re customizing your backups or encountering VSS problems it helps to know more. So let’s take a closer look at VSS, the virtual shadow copy service.
What backup problem does VSS solve?
Backups can take a long time, which is a problem because the data you are backing can be changing, sometimes a lot. This means your backup contains data as it was at different points in time–it is not consistent. This inconsistency causes problems for data, especially application data like databases that a constantly changing as shown in the example below.
VSS solves the inconsistent data problem by creating and maintaining a point–in–time snapshot of the volume to be backed up. The backup job can then use this snapshot.
VSS can create snapshots with two levels of consistency:
- Crash consistent: A snapshot is created of the selected data›s volume. The snapshot does not include data that is changing or in memory, so data may be missing or inconsistent.
- Application consistent: The application being backed up checks its own files in the snapshot to make sure they are correct. For example, information in memory and uncompleted database transactions are included in the snapshot, making it more accurate and application-consistent.
How does VSS make an application consistent backup
The VSS Service
The VSS service consists of 3 subsystems that interact to create and maintain snapshots. They are:
- The VSS requester: The VSS requester (such as BackupAssist) asks for the snapshot to be created and, when it’s no longer needed, asks for the snapshot to be removed.
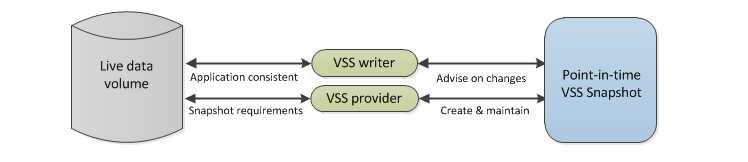
- The VSS writer:A VSS writers allow applications to ensure that their own files (in a snapshot) are application consistent. VSS writers are built into VSS-aware applications such as Exchange and SQL Server.
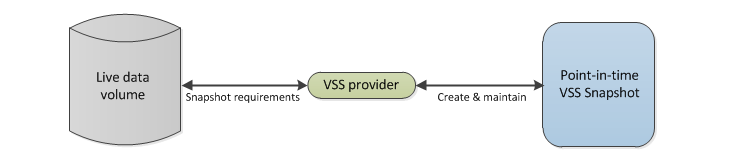
- The VSS provider:The VSS provider creates and maintains snapshots. Microsoft operating systems ship with a VSS provider called the Microsoft VSS provider.
The VSS process in action
Now that you know about the subsystems used by VSS, let’s look at how they work together to create a snapshot. Specifically, we will look at a snapshot created and maintained by a Microsoft VSS provider. The Microsoft VSS provider normally creates a snapshot on the same volume as the live data.
If the live data changes, a copy of the previous version of that data is saved to a location called the shadow storage. By doing this, the snapshot is able to maintain a point–in–time version of the live data, that only requires disk space equivalent to the data that has changed.
So now that you know how the snapshot is maintained, how does the application consistent backup job use it? Simple – The backup job asks the VSS service for the selected data and the following happens:
- If the data HAS changed, the snapshot will provide the backup job with a copy of the data as it was before it changed, from the shadow storage.
- If the data HAS NOT changed, the snapshot will provide the backup job with the data from the live volume.
The process of copying live data before it changes causes a small performance reduction for volume writes. The longer a snapshot is needed, the larger it will become; the more data changes the faster the snapshot grows. The space available for the snapshots must be sufficient to store all changes to the data while the snapshot exists
Let’s break it down, step by step.
The below diagrams depict the communication between the backup software, the data, the snapshot and subsystems. All of this communication is managed by and through the VSS service.
Step 1 The VSS requester (BackupAssist) tells the Microsoft VSS provider service what it needs and to prepare a snapshot.
Step 2 The Microsoft VSS provider will then make the snapshot and maintain it, as the live data changes.
Step 3 So that backups are application consistent, any assigned VSS writers will advise on live data changes to the snapshot.
Step 4 The snapshot is complete and ready to use, and control passes back to BackupAssist, the VSS requester.
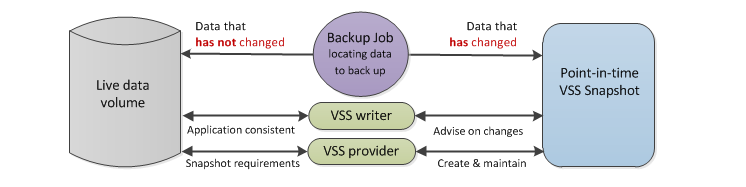
The backup job can now begin requesting data from the VSS service, and create the backup.
Once a VSS aware application like Exchange Server knows that its data has been backed up, its VSS writer will perform some clean–up activities such as clearing its database transaction logs. This can free up disk space and speed up the application.
The application-consistent backup job uses a variable path that points to both the snapshot and the volume the application is on. The VSS service will determine if the file requested by the backup is in the snapshot or the live data. BackupAssist never knows if the data it backed up came from the live data or the snapshot.
How does BackupAssist System Protection use VSS?
Each backup report give you everything you need to know about the report, meaning you can spend less time searching for answers and more time managing systems. Backup reports include start and end times, the backup destination, number of files backed up and the size of the backup, among others.
Another use for the consistency snapshot
System Protection creates a full image backup when it first runs. If the data selection and destination do not change, the next backup will be incremental. This is achieved by reviewing the data to be backed up and the data in the destination – to see what data changed. What has changed, is what is backed up.
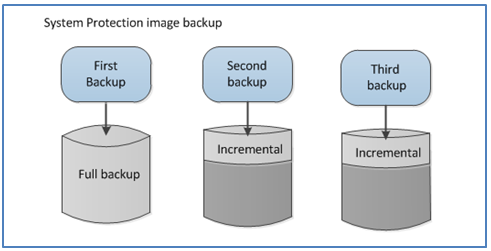
Determining what data has changed consumes a lot of time but BackupAssist can do this quickly using snapshots. A snapshot knows what data has changed, because that is what it maintains. So, instead of deleting the snapshot after a backup, System Protection keeps the snapshot and uses it in the next backup to help identify that data that has changed. This process is called incremental reading.
To maintain a persistent snapshot for incremental reading select the BackupAssist Setting tab > Windows Settings > Enable image tracking.
With incremental reading enabled, a 20 min incremental image backup could be completed in 2 min.
This only works if the destination does not change and if the data selection does not change. For that reason, we advise that the same media is used at least for a week, so the performance gains can be achieved.
System Protection cannot use incremental reading to enable fast incremental backups if the data source is a ReFS formatted drive.
Introducing the historical snapshot
The limitation of image backups is that each backup overwrites data that has changed, so you can only restore data from the previous backup. The only way to create a restore point for every backup would be to create a full image backup each time the job runs, and that would waste time and disk space.
This limitation is overcome by creating a persistent ‹historical snapshot›, on the backup destination. A historical snapshot is created before the backup jobs runs. This is a snapshot of the backup itself, so when the backup job then incrementally overwrites data in the backup, the historical snapshot maintains a copy of the data that was changed.
This means that when a restore is performed, either the image backup or any of these historical snapshots can be used to provide a restore point for any point in time that a backup job ran.
It is important to understand that the historical snapshots are stored on the same disk as the backup. The space on the disk used by the snapshot to store data is called the volume shadow copy storage. When the amount of disk space allocated to the shadow copy storage reaches its limit, it will delete the oldest data to make room for new data.
For this reason, you should:
- Only use this destination for backups
- Set the disk space allocated to your shadow copy to a size that allows for it to grow as data is added.
Only backup destinations that are seen as local devices by the computer you’re backing up can support historical snapshots. These destinations include local hard drives, iSCSI targets, external hard disk drives (that are directly attached) and BackupAssist Data containers.
To learn more about creating an application-consistent backup, visit BackupAssist.com


